Hainosaurus boubker
Introduction
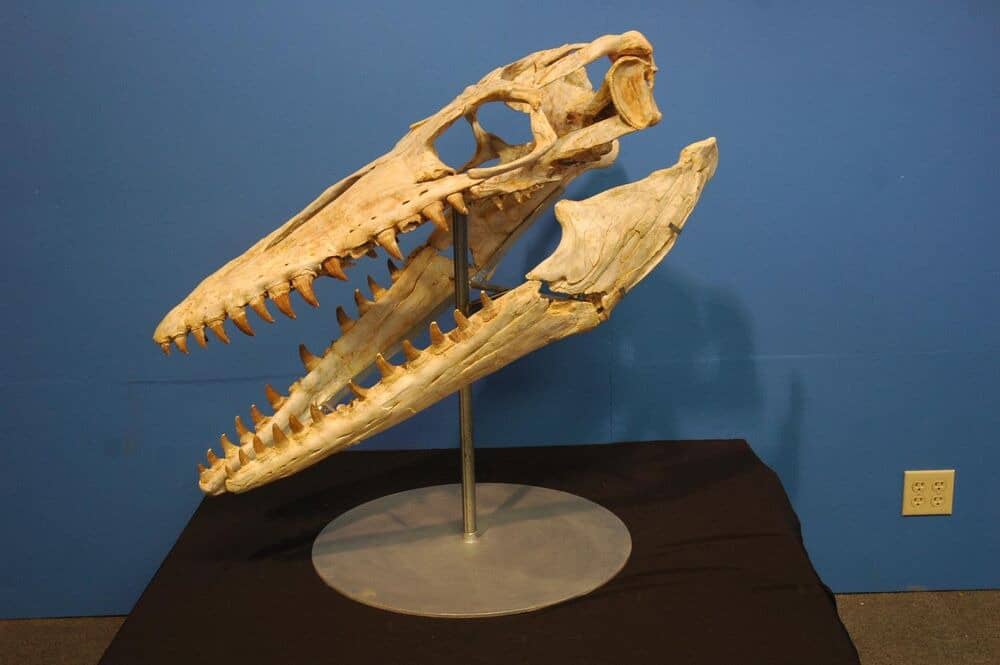
Hainosaurus boubker, a newly identified tylosaurine mosasaurid, has been discovered in the Sidi Chennane Phosphate quarry near Oued Zem, Morocco. This remarkable species was among the largest mosasaurs, measuring approximately 8 to 12 meters in length. What sets Hainosaurus boubker apart from other tylosaurine mosasaurids is its unique blade-like teeth, which are laterally compressed, surrounded by enamel facets, and differentiated along the dental margin.
Significance of the Finding
The significance of this finding lies in the fact that Hainosaurus boubker represents both the youngest species of Tylosaurinae and the first occurrence of this group in North Africa. Boubker Chaibi, a local fossil enthusiast, initially discovered an unusual bone that was later identified as the distinct toothless rostrum of a tylosaur. After generously donating the specimen for further study, the species was named in his honor.
Diversity in the Maastrichtian Deposits
The Cretaceous Phosphates of Morocco, specifically the Maastrichtian deposits, preserve the highest diversity of mosasaurid squamates found anywhere in the world. Decades of intensive sampling have revealed at least ten genera and thirteen species belonging to the mosasaur subgroups Halisauromorpha, Plioplatecarpinae, and Mosasaurinae. Notably absent from this assemblage are members of the macropredatory Tylosaurinae. The scarcity of Tylosaurinae in the Maastrichtian has been previously attributed to factors such as collecting bias, ecological preferences for deeper waters, or habitat limitations to higher paleolatitudes.
Feeding Strategy and Hunting Abilities
The discovery of Hainosaurus boubker in deeper water deposits suggests that it was an open water predator with an opportunistic feeding strategy, preying on various available food sources. Its large size and knife-like teeth would have been advantageous for capturing and consuming large prey, including fish and other marine reptiles. With its elongated, snake-like body, Hainosaurus boubker possessed exceptional swimming abilities, enabling it to engage in fast pursuit and ambush hunting.
Tooth Characteristics and Distribution
The dentary of Hainosaurus boubker exhibits 13 teeth, while the maxillary contains 14 teeth. Notably, the teeth found in Morocco are generally very dark brown in color, feature smooth enamel surfaces, and lack serrations. While these teeth are rare in the Sidi Daoui Couche 3 deposits, they are more frequently found in the Sidi Chennane locality.
Classification Debate
It is worth mentioning that Hainosaurus is widely accepted as a valid genus by paleontologists worldwide, although there is ongoing debate among North American researchers regarding its classification.